Fiber optic cable connectors are essential components in fiber optic networks, providing the means to connect the fiber optic cables to networking equipment. Here’s an overview of what fiber optic connectors are, their types, and how they work in an internet setup:
What Are Fiber Optic Cable Connectors?
Fiber optic connectors are used to join fiber optic cables to other devices such as routers, switches, modems, or even other fiber optic cables. These connectors allow for the transfer of data via light signals through the fiber strands. The connectors ensure that the fiber optic cable is securely attached to devices, maintaining a clear path for high-speed data transmission.
Key Characteristics of Fiber Optic Connectors:
- Precision: Fiber optic connectors must align the small glass fibers precisely to ensure optimal signal transmission. Any misalignment can result in signal loss or degradation.
- Low Loss: Fiber optic connectors are designed to minimize the loss of light (and thus data), ensuring high-quality, fast internet speeds.
- Durability: Fiber optic connectors need to be resistant to wear and tear, environmental conditions, and physical stress.
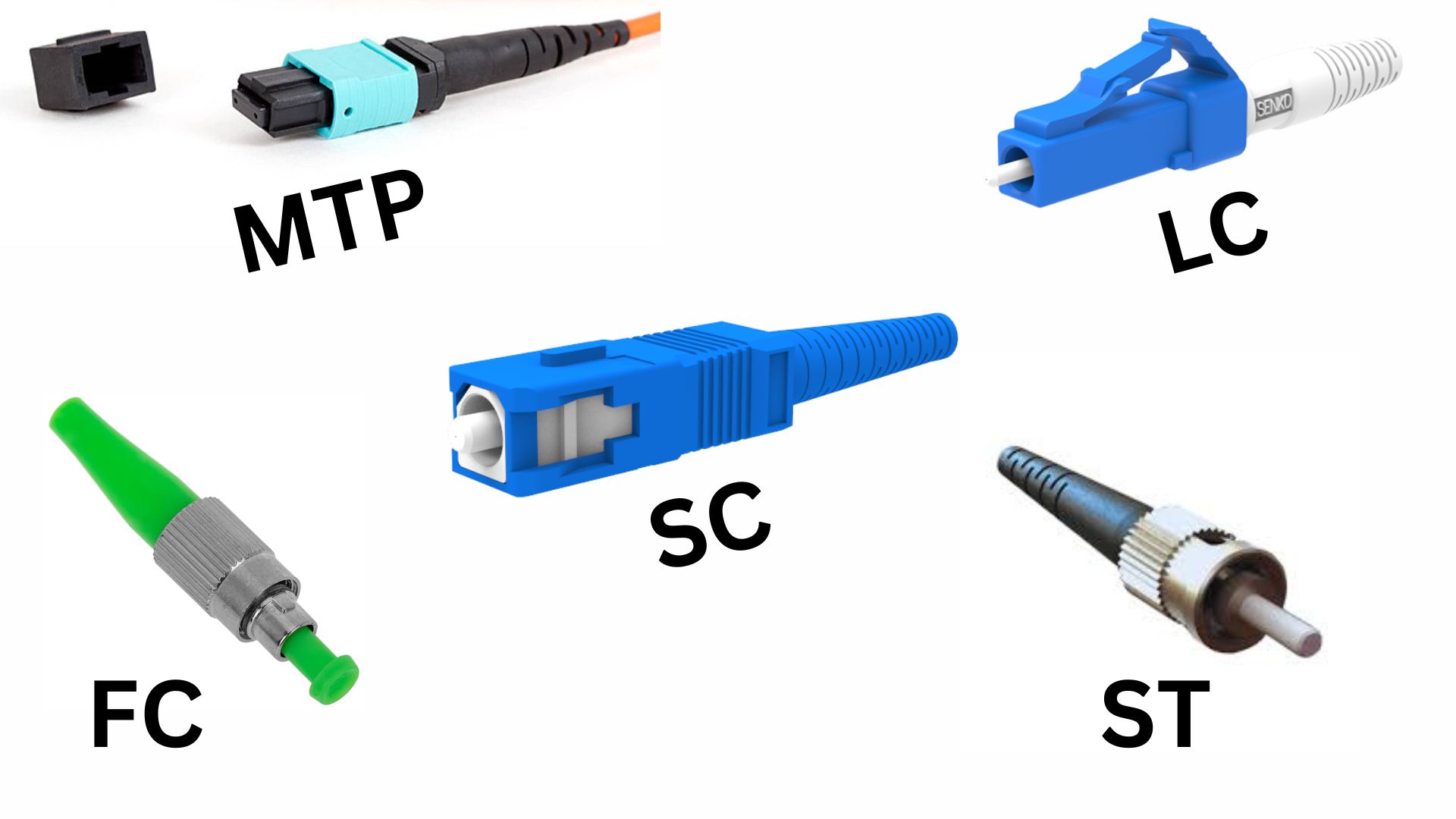
Common Types of Fiber Optic Connectors
There are various types of fiber optic connectors, and their selection depends on the type of fiber optic cable and the networking application. Below are some common types:
- SC (Subscriber Connector):
- Design: Push-pull design with a square shape.
- Use: Common in data communication, telecommunication, and broadband applications.
- Benefits: Easy to use and widely adopted, providing stable and reliable connections.
- LC (Lucent Connector):
- Design: Smaller, compact version of SC connectors.
- Use: Often used in high-density applications like data centers.
- Benefits: Smaller size allows more connections in a limited space, great for environments where space is a premium.
- ST (Straight Tip):
- Design: A bayonet-style connector, meaning it locks in place with a twist.
- Use: Commonly used in legacy systems or older telecommunications infrastructure.
- Benefits: Simple and secure connection, but larger than newer designs like SC or LC.
- MTP/MPO (Multi-fiber Termination Push-on):
- Design: Multi-fiber connectors that can connect multiple fibers at once (typically 12 or 24 fibers).
- Use: High-density applications like large data centers or enterprise networks.
- Benefits: Significant reduction in the number of cables and connectors needed, making installations more efficient. Detail
- FC (Ferrule Connector):
- Design: Features a threaded connector for a secure fit.
- Use: Typically used in high-precision environments like laboratory settings.
- Benefits: Secure connection with low signal loss, ideal for high-performance environments.
Fiber Optic Cable Types:
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF):
- Design: Carries a single ray of light down the fiber core.
- Use: Used for long-distance communication due to its low attenuation (signal loss) and higher bandwidth.
- Connectors: SC, LC, FC, and MTP/MPO connectors are commonly used with single-mode fiber.
- Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF):
- Design: Allows multiple light rays to travel down the fiber core, typically over shorter distances.
- Use: Used for local area networks (LANs) and data center connections.
- Connectors: SC, LC, and ST connectors are commonly used with multi-mode fiber.
How Fiber Optic Cable Connectors Work:
- Connecting the Cable: The fiber optic connector fits into the fiber optic cable at the end, either crimped, glued, or mechanically spliced, depending on the type of connector.
- Aligning the Fiber: The connector houses a ferrule (small tube) that holds the fiber in place, ensuring precise alignment for optimal signal transmission.
- Light Transmission: The signal, in the form of light, travels through the fiber and into the connector, where it is transferred into the receiving equipment, such as a router or switch.
- Sealing and Protecting: Many fiber optic connectors are designed to seal the fiber from dust, moisture, and other environmental factors to prevent signal degradation.
Benefits of Fiber Optic Connectors in Internet Connectivity:
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Fiber optic cables are capable of transmitting data at extremely high speeds, with minimal latency. Connectors ensure the integrity of these fast speeds.
- Large Bandwidth: Fiber optics provide a much larger bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables, supporting more data to be transmitted at once. This is crucial for modern internet usage, such as streaming, gaming, and video conferencing.
- Longer Distances: Fiber optics can carry signals over much longer distances without losing signal quality, making them ideal for both local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
- Future-Proofing: As internet speeds continue to increase, fiber optic connections remain relevant and capable of handling the growing demands of high-speed internet.
Conclusion:
Fiber optic connectors are an essential part of any fiber optic internet setup, ensuring reliable, fast, and high-quality data transmission. Choosing the right type of connector depends on your specific needs, such as the distance of the connection, the environment, and the number of fibers required. They play a key role in achieving high-speed internet connectivity, essential for both home and business applications.